Low-code use cases are limitless and applicable across different industries, where they transform the way businesses solve problems and innovate. This article covers these use cases and portrays how effective and flexible low-code platforms are in facilitating a digital transformation journey.
Key insights
- Low-code development enables fast, less expensive app design using pre-made components
- You can develop using low code with relatively few people, and they don’t need in-depth knowledge of coding languages
- Low-code development works for a range of apps, such as modernizing legacy apps, automation, data integration, customer relationship management (CRM) and sales, and business intelligence
- With Visual LANSA, you can develop a wide range of progressive web apps, mobile apps, ERPs, e-commerce solutions, and application portals
What Is Low Code Development?
Low-code development is an approach to building applications using drag-and-drop, visual, pre-built components. With these tools, users with relatively little coding knowledge can build fully functional apps — all without having to use a coding language.
Learn more about low code development.
Common Low Code Use Cases
The following low code platform use cases work across many industries, making this approach versatile enough to suit the needs of thousands of business models.
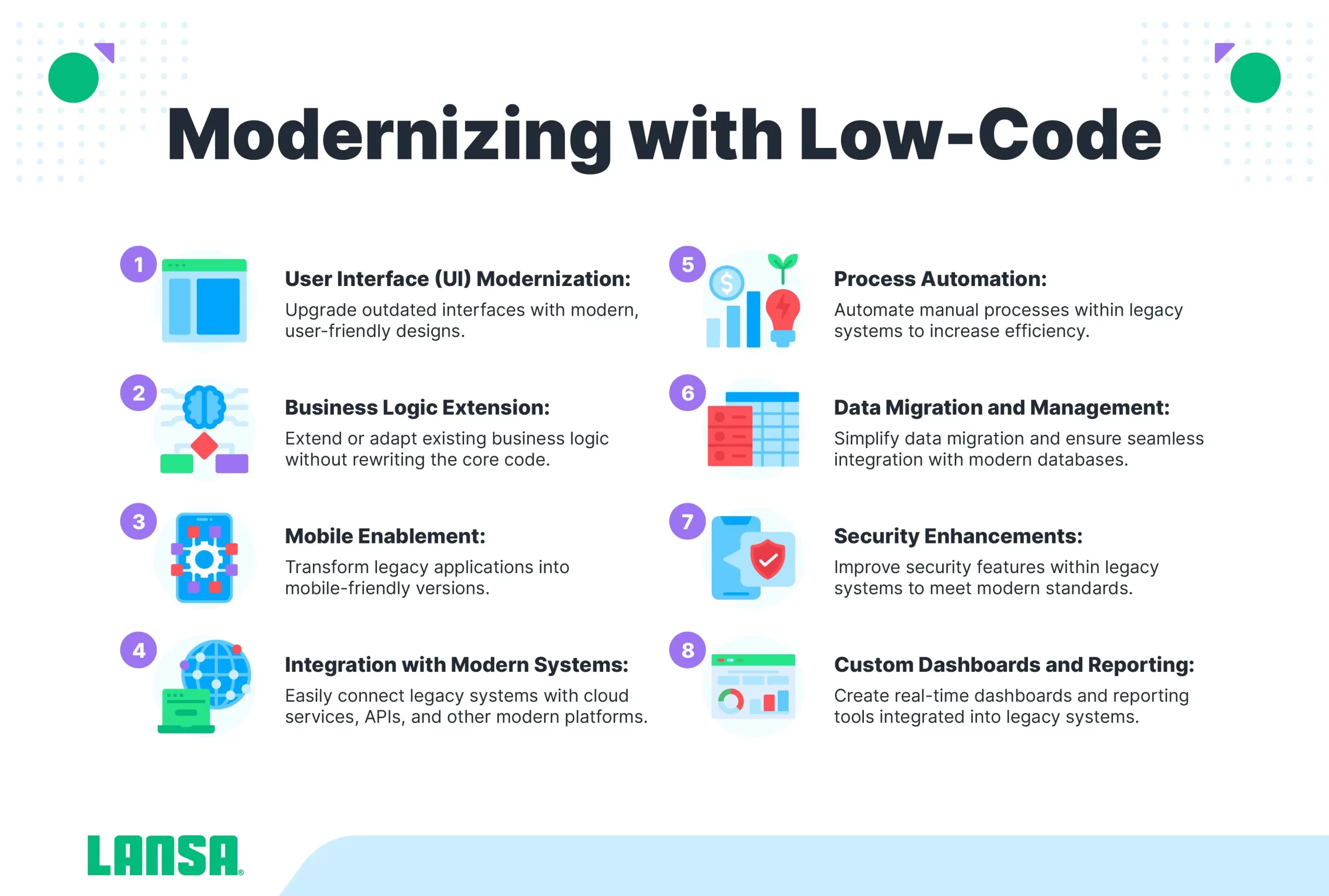
Legacy Application Modernization
Legacy application modernization is the transformation and updating of legacy apps so they can work with modern architecture. It is one of the most common low code examples because so many organizations need to transition legacy apps so they work with their current infrastructure.
There are multiple ways to modernize legacy apps. For example, a rapid application modernization process (RAMP) involves consolidating an app’s current functionality and combining it with new capabilities. You perform RAMP in stages, incrementally modernizing your solution in a way that minimizes the impact on your operations.
You can also use LANSA’s aXes, which enables you to transform IBM I 5250 applications without changing your source code or using any modern coding languages. You can quickly change how your screens look and feel using drop-downs, button themes, and more. Using aXes, you can take an older 5250 app and add functionalities, such as mobile capabilities in far less time than it would take using traditional, high-code development.
Business Process Automation and Integration
Business process automation involves getting rid of manual, time-consuming, and paper-based processes, replacing them with automation. This is another one of the more popular low-code use cases because it saves teams so much time and energy, while simultaneously reducing the chances of human error.
Application and business data integration focuses on combining data from disparate sources and using it to build applications or perform analysis. The potential for business process integrations is almost incalculable because you can automatically pull and analyze data, building robust analytical solutions.
Rapid Prototyping and Development
With low-code tools, you can build apps far faster, thanks to the pre-build components at your disposal. As a result, mobile, progressive, and rapid application development lifecycles are shorter — without sacrificing app quality.
For instance, with Visual LANSA, you can create app prototypes in a matter of minutes, build end-to-end solutions, and speed up digital transformations.
Data Integration and Management
Data integration centers around pinpointing the data you need and then pulling it into whichever system can benefit from it. In this way, you break down siloes that would otherwise force analysts and other employees to manually dig out the information they need to make decisions.
With data management, you enable a more efficient application and business data integration solution. By pulling, cleaning, and otherwise transforming business data, you prepare it for integration, presenting it in a way applications and decision-makers can better use it.
CRM Systems and Sales Automation
You can use low-code solutions to improve customer relationship management systems. This enables you to automate sales processes, boost sales efficiency, and enhance customer engagement.
Supply Chain Management
One of the more compelling low-code examples is creating supply chain and logistics management systems because they can be so effective at boosting efficiency and reducing costs. By digitally transforming your supply chain, you can improve your distribution, inventory management, and overall logistics processes.
Business Intelligence Reporting and Analytics
You can use low code to build BI reports that improve your analytics and reporting. This gives you powerful business intelligence tools designed to make more effective, data-supported decisions.
Compliance and Risk Management
As the compliance landscape evolves, you can avoid falling out of line by developing solutions that automate your compliance management. Low code is equally effective for creating internal governance and risk assessment and management systems. Your risk management teams can build solutions on their own, without having to hire an external developer.
Custom Applications
Building custom applications with low code is less time- and resource-intensive because you have pre-made tools at your disposal. This simplifies the way your apps are developed, making it possible to create more iterations faster and address issues quicker.
IoT Integration
You can take applications you build with low code and integrate them with your IoT platforms. You can also integrate your low code-built solutions with third-party services and enterprise systems. As a result, your organization gets data they can use to generate business-critical insights.
Whether it’s sensors that read patient biometrics, equipment-tracking tools, or scanners that read and interpret barcodes, integrating IoT devices with low code-designed solutions is efficient and seamless.
Monolithic Applications to Microservices
Microservices, which refer to components of applications that perform certain business functions, are relatively easy to design using a low-code platform. You can use APIs to transform monolithic apps into microservices. In this way, you make their functions available to many different applications or features of a single app.
Examples of Apps You Can Build With Low Code
The types of apps you can create with low code are only limited by the platform you choose. Here are some of the most common examples.
Mobile Apps
You don’t need a team of professional programmers for mobile app development when you use a low-code platform. For instance, with Visual LANSA, you can develop applications for mobile users via a dependable integrated development environment (IDE).
For example, many take advantage of a mobile app-building solution like LongRange, which enables users to use low code while designing apps that take advantage of mobile device-specific features such as GPS, local storage, and cameras.
Progressive Web Apps
You can create progressive web apps (PWAs), which deliver services through the web, with low-code solutions in much less time than it would take with traditional coding.
Whether you’re just getting started with PWAs or have been building them for years, low code can give you a faster, more streamlined process. By simplifying the way you develop PWAs with low code, you build products faster and speed up their testing and implementation.
E-commerce Solutions
A low-code development solution is a powerful alternative to other, sometimes restrictive, options like Amazon or eBay. These often don’t have all the features a business needs, whether it’s supply chain monitoring, tracking deliveries, or managing orders.
A solution like LANSA Commerce Edition, on the other hand, gives you the flexibility to configure your app to fit exactly what your company needs. You can design tools for marketing, cart checkout and management, customer service, and more, depending on your requirements.
Application Portals
Application portals make it possible for users to execute basic actions without your help. Instead of taking up your IT team’s time, users can look up articles, make changes to their profile, get quotes, or search through your products on their own.
For example, you can easily build and deploy powerful manufacturing portals with low code using LANSA’s Portalize. It comes with out-of-the-box portal features, making creating B2B, B2C, learning, partner, self-service, and community portals easy.
ERP Systems
With the right low-code solution, you can customize your enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools. Despite the complexity, a low-code platform can give you ERP frameworks that make it easy to change your ERP along with the needs of your business or the market.
The Best Low-Code Tool: Visual LANSA
Visual LANSA is an ideal low-code solution for scaling and streamlining your development process. With Visual LANSA, you get:
- Faster development cycles. You can create apps 10 times faster with Visual LANSA’s pre-built modules.
- Improved time-to-market. You accelerate your dev lifecycle as you create more iterations in less time.
- The ability to use fewer resources. There’s no need to rely on a big development team with deep coding knowledge because Visual LANSA gives you one solution for both front- and back-end development.
- Greater business agility. Visual LANSA’s flexibility and adaptability make it a good solution for businesses with changing needs.
Industries That Benefit From Low Code Development
Industries that benefit the most from low code often leverage it to the fullest. Here are some of the most common types and how they do it.
SaaS
SaaS companies can use low code to both produce new solutions and create apps to manage their internal processes.
Healthcare
Healthcare organizations leverage low code for building apps that collect and process patient data from IoT devices, as well as managing scheduling and other human resource challenges.
Education
Educational institutions benefit from low-code platforms by creating solutions custom-designed to meet the needs of specific groups of students and teachers. For instance, a single school district can build multiple apps to manage unique student populations based on grade level.
Logistics
Logistics companies use low code to pull in shipping, fulfillment, and inventory data in real-time, discovering ways to speed up processes and get goods to customers more efficiently.
Finance
Finance companies design dashboards and other analytical tools that integrate data from multiple financial processes, making it easier for analysts to help clients and internal stakeholders make decisions.
E-commerce
E-commerce companies use low-code platforms to build customized product catalogs, shopping carts, inventory management systems, and customer service portals.
Retail
Retailers can build customer-facing applications, point-of-sale systems, and reporting and analytics solutions that save employees time and pave the way for deeper analytics.
Use Low Code to Add Agility and Speed to Your Dev Processes
The above use cases are just a few examples of what’s possible when you can create solutions using pre-built components. The true potential of low code is limited only by your imagination and business goals. Visual LANSA expands the possibilities of low code by giving you the ability to build cross-platform, robust applications using a single repository definition markup language (RDML). Contact us to learn more.