The AS/400 is a family of midrange computers that IBM introduced back in 1988. Even today, It still continues to serve many businesses because it is known for reliability, scalability and secure performance. The AS400 (Now IBM i) remains a key tool for managing critical applications in fields like healthcare, financial services, retail and manufacturing.
The AS400 uses a special technology called Technology Independent Machine Interface (TIMI).
So what exactly is TIMI?
Think of it as a “Translator” that allows programs to speak using common language, no matter what type of computer chip (processor) is inside.
This means IBM i (AS/400) can upgrade the computer’s processor without rewriting their programs. The TIMI acts like a middle layer that converts software instructions into a format and adjusts the instructions to match the new processor, so old programs keep working on new hardware without any changes.
This ensures that the programs on AS400 are running smoothly even if the hardware is upgraded, without disrupting existing applications.
Although AS400 software was developed at the end of the last century, it is still popular and frequently used today. In this article, we will look at what AS400 is, what are the benefits of using it, its scope, and also what alternative names exist. We will also explain how to upgrade an older IBM green screen.
What is AS400? The Legacy
The AS400 also known as IBM i series or IBM i is a mid-range computer system designed to serve as an integrated platform for business and enterprise applications.
As stated above, it is widely known for its reliability, scalability and security which made it (and makes it) an attractive choice for the businesses and enterprises that needed a system to handle complex business workloads.
How is AS400 referred to?
AS400 is familiar within the market and among business professionals for several names which often creates confusion for those who are not familiar with its history. So here are some of the most common terms used:
- AS/400
The original name was given by IBM in 1988.
- IBM iSeries
A rebranding that took place in the early 2000s.
- IBM i
The current brand name for the operating system that runs on the platform.
- System i
Used in some contexts as a shorthand reference for the iSeries.
- AS400 Software
A common way to refer to the software used on the system.
All these different terms point to the same powerful system (AS-400). Though the name may differ depending on when it was introduced or updated.
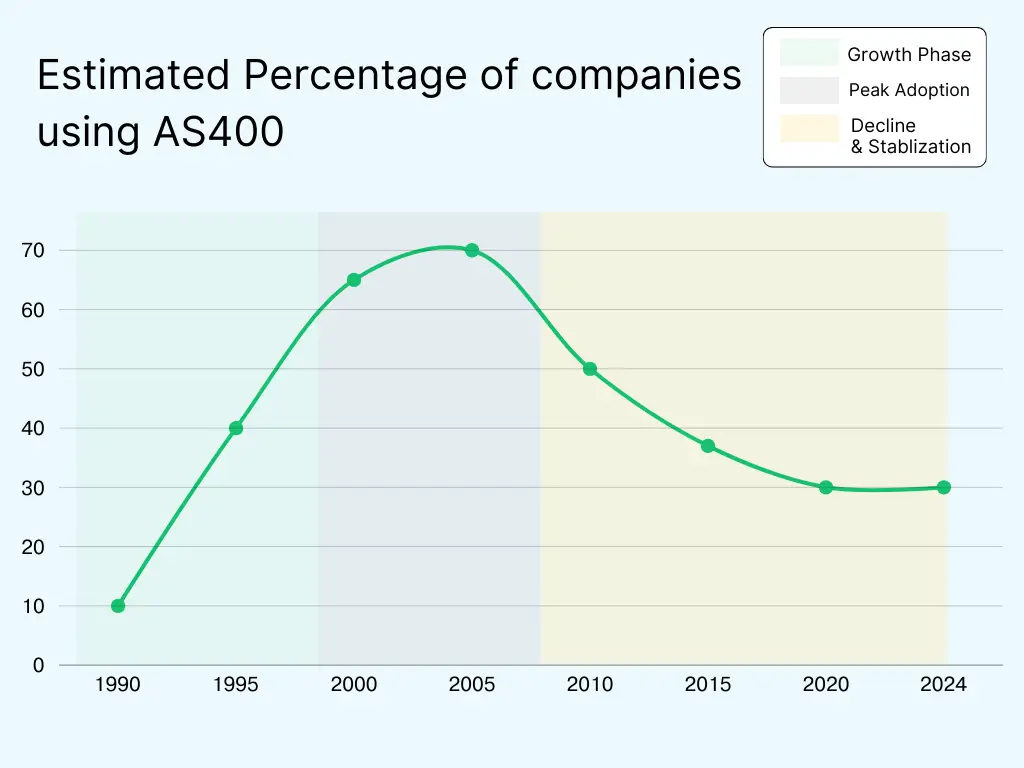
History and evolution of AS400
The AS400 (Application system/400) has been a cornerstone of enterprise computing for decades. This flexible platform (now known as IBM i) was first created to give companies a dependable, all-in-one solution for managing their systems infrastructure, data and applications. After going through multiple iterations and enhancements, AS400 has transformed from a hardware system into a more adaptable and contemporary solution that is still used by businesses (and large enterprises) all over the world.
In fact, the AS400 was first introduced as IBM AS400 but the system was rebranded as technology developed throughout time and its name kept changing to reflect these advancements.
It was later rebranded to IBM iSeries in the early 2000s, followed by IBM System i. Now it is known as IBM i because of its ongoing role as an integrated platform for enterprise computing.
The Evolution of AS400
Throughout its journey, AS400 has been updated to meet the changing needs of businesses.
The key upgrades have typically focused on:
Hardware enhancements
Increased processing power and…
Improving integration with modern technologies.
Below is a table summarizing the evolution of the AS400 system, including the year, hardware name and the operating system (OS) used.
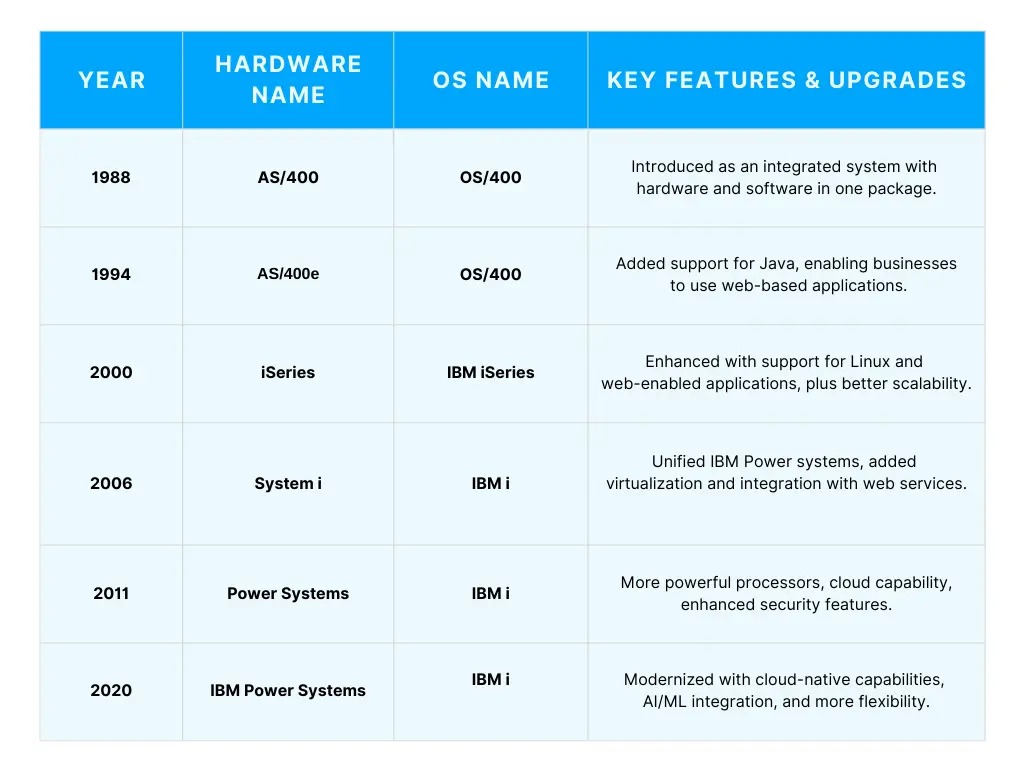
IBM has continually improved the AS400 (now IBM i) with enhancements to both hardware and software. Here’s how:
Initial Release (1988)
The AS400 system was a multifunctional solution integrating hardware, software and database management. It featured an OS/400 operating system and became popular for its reliability.
- Early 1990s
Support for Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and Java was introduced, making the system more adaptable to changing programming trends. This opened up the AS400 to a wider variety of enterprise applications.
- 2000s (iSeries and System i)
During this time, AS400 evolved into the iSeries and System i lines. Important upgrades included support for Linux and web applications, making it easier for companies to integrate new technology into their existing infrastructure.
- 2010s (IBM Power Systems)
This phase saw increased emphasis on cloud integration, virtualization and AI capabilities which helped IBM i better support modern business needs.
The introduction of IBM Cloud capabilities made AS400 an even more attractive option for businesses looking to modernize their systems.
Present-Day (IBM i)
Today, IBM i continues to thrive, offering businesses a flexible platform for handling mission-critical operations. It supports everything from traditional workloads to cloud-based and AI-enhanced applications.
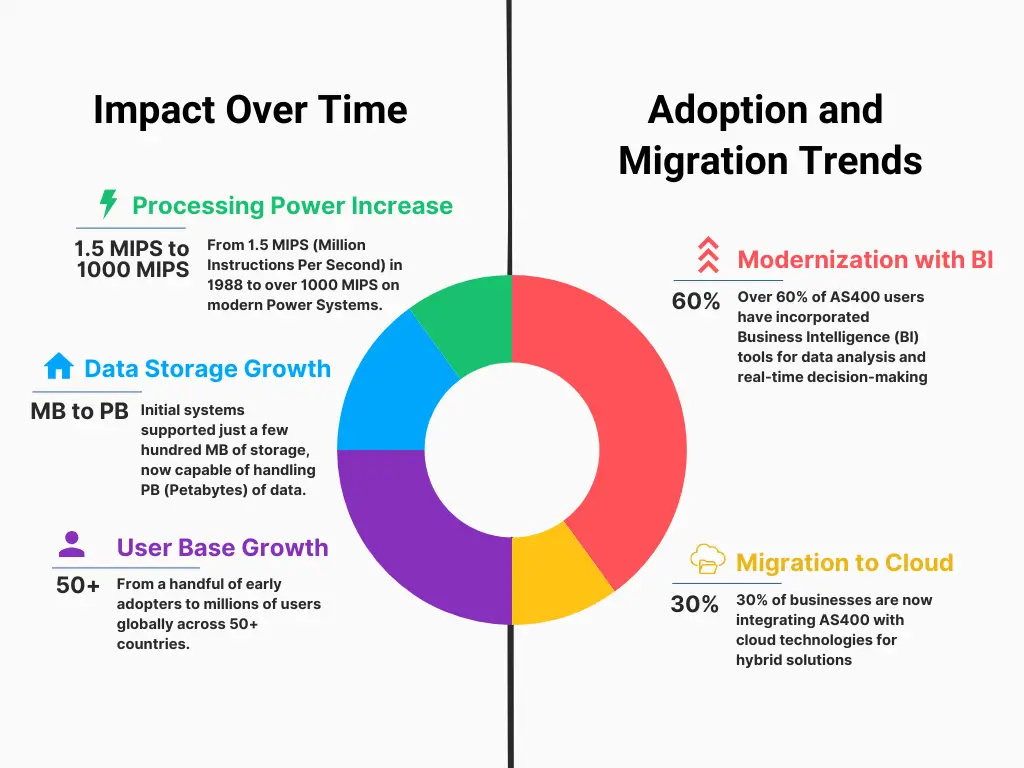
AS400 in Numbers: Statistics and Usage
Languages supported by AS/400 (IBM i)
One of the prominent features of AS/400 is its programming environment. The system supports several languages, making it an all-in-one platform for creating business applications.
Here are some of the main languages supported by AS/400 systems:
- RPG (Report Program Generator)
A programming language that’s been around since the early days of the AS/400. RPG is particularly known for handling business applications efficiently.
- COBOL
Commonly used for legacy business applications, especially in finance and government sectors.
- Java
IBM i supports Java, making it possible to run modern applications on the system.
- SQL
For database management and querying, SQL is fully integrated into the AS/400 environment.
- CL (Control Language)
A scripting language used to automate system tasks and operations.
This combination of languages enables businesses to integrate both legacy and modern systems, which is one reason AS/400 remains a viable solution today.
Key Characteristics of AS/400 Software
AS/400 software or IBM i has several key features that make it stand out in the world of enterprise computing. Some of them are as follows:
- Reliability
Known for its uptime and stability, AS/400 is often used for mission-critical business applications.
- Security
The system has security features that are integral to industries like finance, healthcare and government.
- Integrated System
AS/400 was designed as a complete solution, combining hardware, operating system and application support into one system.
- Scalability
AS/400 systems can scale as business needs grow, making them suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises.
- Backward Compatibility
IBM ensures that older applications built on the AS/400 remain operational on modern systems, ensuring businesses don’t lose their investments in legacy software.
These characteristics have allowed AS/400 to endure, even as other systems have come and gone.
What is the difference between IBM i and AS400?
IBM rebranded the AS/400 system, but many still refer to it by its original name. So what exactly is the difference between IBM i and AS/400?
Here’s a quick breakdown
AS/400 (1988)
- Original System
AS/400 was introduced as an integrated hardware and OS solution specifically for mid-sized businesses, offering strong data handling capabilities.
- Business-Ready Stability
Known for exceptional uptime, AS/400 gained popularity for running critical business applications due to its reliable performance and in-built security.
- Integrated Database
AS/400 featured an embedded DB2 database, eliminating the need for external databases and simplifying data management.
- Limited Web Compatibility
Primarily a transactional system, AS/400 lacked the web and mobile flexibility required by today’s technology needs and requirements.
IBM i on Power Systems (2008 – Present)
- Updated OS for Power Systems
IBM i continues the AS/400 legacy on modern Power Systems hardware, supporting a wider range of business operations.
- Adaptable to Cloud and AI
Unlike the original AS/400, IBM i supports cloud applications and AI capabilities allowing businesses to integrate newer technologies.
- Advanced Resource Management
IBM i introduces robust virtualization, enabling multiple OS environments on a single system which optimizes resource use.
- Enhanced Data Security
With stronger security protocols, IBM i addresses current compliance needs, meeting industry standards for data protection.
These key differences highlight how IBM i has evolved and how it remains a continuation of the AS/400’s legacy, offering backward compatibility with older AS/400 applications.
Mainframes And IBM i (AS/400) Systems: What’s The Difference?
There are many differences between mainframes and IBM i (AS/400) systems. Instruction set and underlying hardware, scalability, user interface, general architecture, etc. But the main difference is that IBM i is a mid-range server and the mainframe is a high-end server.
A mid-range server is a more affordable but less powerful option than a high-end server such as a mainframe. Another difference is that the mid-tier server is a stand-alone system, while the mainframe is a distributed network of components that interact to form a massive computing platform. Companies use a high-performance server to store large amounts of data and run centralization applications. It is distinguished by reliability and safety.
Is the AS/400 Still in Use?
The IBM AS/400 system is constantly evolving and using modern technologies. Many of the world’s leading companies are now using it for mission-critical applications. This system provides scalability, security, reliability, and flexibility. AS/400 powers ERP systems, and applications for hospitals, banks, government agencies, and more.
Here are some key reasons why the AS/400 system is still in use:
- Reliability and Security
The system offers a secure, integrated database with high transaction speed, making it ideal for data-intensive applications.
- Scalability and Performance
AS/400 is known for its powerful processors, delivering performance three to five times greater than comparable systems, which is essential for businesses requiring high productivity.
- Interoperability
Applications developed in the 1980s can still run unchanged on newer hardware, ensuring longevity and reducing the cost of redevelopment.
- Modern Technology Integration
IBM i incorporates in-demand technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and client-server systems using modern programming languages like Java and C#.
- Logical Partitioning (LPAR)
This feature allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously on a single device, ensuring resource independence and optimized performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness
Switching from AS/400 to another system can be costly and disruptive, which encourages businesses to retain their existing systems.
For a deeper look at why the AS/400 remains a preferred choice in many industries, check out this detailed guide on the continued demand for AS/400.
What is AS400 used for?
The AS/400 system is primarily used to run business applications that require high levels of security, reliability, and scalability. Some of the most common applications of AS/400 include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) SystemsIBM i excels as a foundation for ERP applications, the backbone of managing essential business operations like finance, accounting, HR and inventory.
Companies rely on IBM i to power ERP systems such as JD Edwards, Infor and Lawson.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) SystemsCRM platforms hosted on IBM i enhance customer interactions by tracking data, managing leads, and improving service quality.
They enable businesses to build and maintain stronger client relationships.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM) SystemsOptimizing the supply chain is seamless with IBM i, as it facilitates inventory control, order processing, logistics and demand planning, ensuring smoother operations and higher efficiency.
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)In manufacturing, IBM i supports MES tools that monitor production processes, manage work orders and uphold quality standards, contributing to streamlined shop floor operations.
- Healthcare Information SystemsIBM i’s role in healthcare includes hosting systems for electronic health records (EHR), hospital information and billing processes, ensuring secure and reliable data handling in a critical industry.
- Banking and Financial ApplicationsFrom core banking to credit card processing and EFT services, IBM i provides the stability and security required for financial institutions to manage complex operations.
- Retail Point of Sale (POS) SystemsRetailers leverage IBM i to power POS systems that enable real-time transaction processing, inventory management, and sales tracking, enhancing customer service and operational transparency.
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)For warehousing, IBM i supports solutions like Manhattan Associates and Royal4, helping businesses manage inventory and streamline fulfillment processes effectively.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and ReportingIBM i brings data to life with BI tools that deliver actionable insights through analytics, interactive dashboards, and comprehensive reporting, driving informed decision-making.
- Document Management and ArchivingDocument management systems hosted on IBM i ensure secure storage, easy access, and efficient handling of critical business documents.
- Transportation and Logistics SystemsFleet operations, shipment tracking, and route optimization in transportation and logistics sectors are made efficient with IBM i-powered applications.
- Utility Billing SystemsIBM i supports utilities by managing billing processes and customer data for essential services like electricity, water, and gas, ensuring accurate and reliable systems.
- Insurance Policy ManagementInsurance providers rely on IBM i for policy administration, claims processing, and underwriting functions, delivering secure and efficient operations.
- Government and Public Sector ApplicationsIBM i supports government services ranging from tax administration to public safety systems, empowering agencies to manage resources and serve citizens effectively.
- Educational Management SystemsEducational institutions use IBM i for managing student information, grading, course registration, and administrative tasks, ensuring seamless academic operations.
The ability to handle such critical applications across different industries showcases the AS/400’s versatility and enduring value.
Modern AS/400 Software Applications
Some of the modern applications include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software
AS/400 systems continue to support ERP applications like SAP, Oracle, and others.
- CRM Systems
Customer relationship management software is now fully compatible with IBM i, offering organizations a way to manage customer data more effectively.
- Web and Mobile Applications
IBM i supports web and mobile application frameworks, allowing businesses to create responsive, user-friendly applications.
These advancements allow businesses to keep their AS/400 systems up to date with the latest technologies.
The Benefits of AS/400
The AS/400 continues to be popular due to several key benefits:
- Reliability
AS/400 is known for its 99.9% uptime, which is crucial for businesses that cannot afford system downtimes.
- Security
AS/400 offers advanced security features to protect sensitive business data.
- Cost-Effective
Compared to newer systems, AS/400 often proves to be a more affordable solution for many businesses.
- Long-Term Support
IBM continues to provide support for AS/400 users, ensuring that their systems remain secure and up-to-date.
The Challenges with AS400
Despite its reliability, the AS400 (IBM i) system has several challenges that modern enterprises face.
Here are some common challenges and solutions, along with how LANSA can assist:
User Interface Limitations
The traditional AS400 system uses a “green screen” interface which is outdated and can be difficult for new users to navigate. These green screens were originally designed with text-only displays, making them less user-friendly compared to modern graphical interfaces.
This can be solved by modernizing the UI by implementing web-based frameworks like Angular or React, which enables a smoother and visually appealing experience.
LANSA can support this by providing tools to streamline the process of transforming AS400 applications into web-based applications enhancing accessibility and usability.
High maintenance costs
Maintaining AS400 systems is costly due to specialized hardware and software.
Moving applications to the cloud can reduce these expenses.
LANSA facilitates a hybrid approach, enabling cloud migration while ensuring seamless integration with on-premise AS400 systems
Difficulty integrating with modern applications
The AS400 system’s design often lacks compatibility with newer software and cloud environments which complicate efforts to integrate with modern business applications.
One approach is to expose AS400 functionality via APIs, allowing it to interact with other applications.
LANSA enables API-based modernization, allowing AS400 data to interact securely with new applications via RESTful APIs.
Programmers.io
A company (Programmers.io) successfully migrated its AS400 applications to the cloud, leading to enhanced scalability, reduced costs and improved system agility.
By leveraging cloud-native solutions, the business experienced greater flexibility in scaling and updating its applications without altering its core AS400 functionality.
Integrative Systems
A project focused on modernizing the UI of AS400 applications resulted in an improved user experience and streamlined operations.
By shifting from green screens to graphical user interfaces, the team could operate more effectively enhancing productivity and user satisfaction.
Modernizing AS/400
IBM has made it easier for businesses to migrate from legacy systems to modern platforms while maintaining compatibility with existing applications.
Key modernization strategies include:
- Cloud Integration
Moving AS/400 systems to the cloud for enhanced scalability and flexibility.
- Web and Mobile Access
Making applications accessible through web browsers and mobile devices.
- Application Upgrades
Upgrading legacy software to take advantage of new features and improvements.
By modernizing their AS/400 systems, businesses can continue to leverage its power while integrating the latest technology.
How To Modernize AS400 With LANSA?
LANSA is a popular solution for modernizing IBM i applications. It provides various tools that make it easy to optimize the application development process, upgrade existing applications, and add new features.
AXes by LANSA is a tool that allows you to easily and quickly create modern user interfaces and web applications instead of the older IBM green screens. All you need to do is use aXes with your IBM i and your employees can securely access their IBM i 5250 applications from any remote device with Internet access
Ready to Modernize Your AS400 Software?
Install a free trial version of aXes by LANSA and use it to modernize AS400 software.