Organizations are looking for IBM i modernization or to modernize their legacy IT infrastructure, particularly their IBM AS400 application servers, also known as ‘IBMi’ or ‘IBM iSeries’ systems. These IBM systems allow different companies to run mission-critical legacy business applications that are expensive to operate and difficult to maintain.
For IBM i modernization, organizations need to adopt emerging modernization approaches and functional design patterns to achieve the maximum scalability, agility, security, and cost reduction benefits. This will also be useful to any IT decision-maker at a company looking to upgrade or modernize their existing AS400 systems.
This guide will give you information about the IBM i/AS400 system modernization. Moreover, we will also discuss different strategies you can use to modernize the hardware/software of an AS400 system.
Existing IBM AS400/IBM i application systems
The IBM i/AS400 application servers have proven robustness, scalability, reliability, security, and low cost of ownership compared to MIPS in IBM Mainframe (also known as ‘IBM z’). The adoption of newer technologies requires a larger set of challenging requirements for AS400 application modernization to maximize the IBM i system’s performance.
What replaced AS400 application systems?
The hardware and the software of AS400 have experienced multiple updates and revisions in name changes. Now, it is replaced with IBM i or IBM System i. While many people still refer to the system as an AS/400 or an iSeries IBM server, it is a Power System that runs an updated operating system known as IBM i or IBM System i.
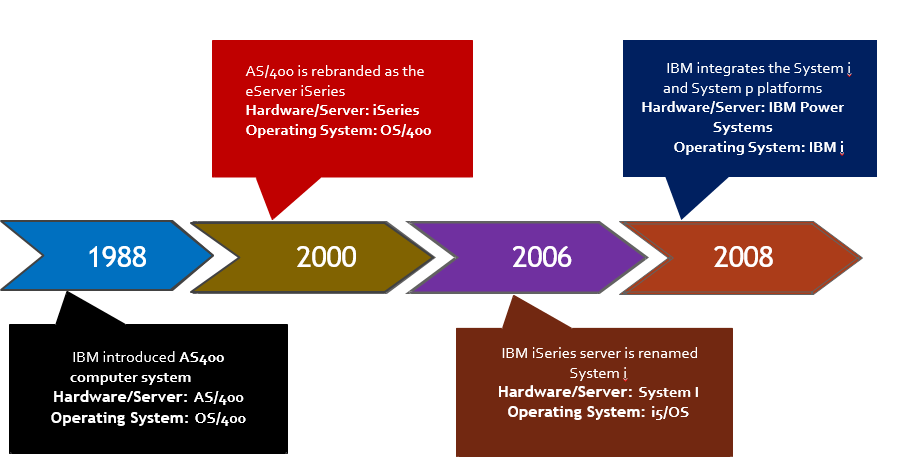
A brief history of As400 / IBM i systems
What is the AS400?
Beginning in 1988, IBM began manufacturing and distributing the AS/400 (Application System/400) line of computers with its own OS/400 operating system and embedded database. They were created by IBM for small and mid-sized organizations due to their scalability, robustness, reliability, security, and low-cost features.
Why is AS400 still used and does it need to be modernized?
Many businesses still use AS400 used for mission-critical systems specific to fields that depend on reliability and stability. It powers vital applications in places like hospitals, banks, and government agencies. Instead of running common applications like employee-based tasks or office functions, AS/400 servers host core applications and ERP systems, that are the backbone of many organizations.
Is AS400 outdated? or Is AS400 in demand?
The AS/400 is often regarded as obsolete, but in reality, it is far from it. The fact that it was introduced to the market in 1988 and has undergone multiple re-brandings hasn’t helped promote the impression that it is a current platform. Despite this, it is still an essential element of many of the world’s top companies’ computer architecture. It has continued to evolve and incorporates demanded technologies nowadays like Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, with new powerful CPUs and software enhancements.
Can AS400 move to the cloud through application modernization?
Yes, you can move AS400 applications to the cloud by using the three different methodology patterns such as Re-Hosting, Re-Engineering, and Re-Architect, etc., to modernize the IBMi/AS400 applications to increase scalability, agility, and performance in the cloud.
Is AS400 user-friendly? Can it be after modernization?
Original 5250 applications are not particularly user-friendly by modern-day standards. Although efficient to many, it features a command line-like user interface (also known as a green screen) that is not particularly appealing to newer generations. Also, they require two types of experts: those who can program it and those who can operate it. Application modernization can help soothe those pains and inject new life into the applications by leveraging the investments of many years and adopting new use cases that exploit web and mobile technologies.
Is AS400 a legacy system ripe for modernization?
The AS/400 or IBM i is not a legacy system, but considering that many of the applications hosted on these systems were created 20 or perhaps 30 years ago, they are likely to benefit from the application modernization tools and techniques available. The assessment of your application strategy versus the current state-of-the-art is a crucial exercise for IT managers nowadays.
What programming language does AS400 use?
RPG is the most extensively used programming language for IBM’s AS/400 series, and it has a long history of functions and capabilities. The COBOL and C/C++ were also used in AS/400 application systems.
What is application modernization?
The practice of upgrading existing software for newer computing methodologies, such as newer languages, frameworks, and infrastructure platforms to modernize IBM i/AS400 applications.
What key challenges arise for AS400 Application Modernization?
Every organization that uses AS400 systems wants to make use of the massive amount of valuable data that is stored within. Unfortunately, limitations such as the code-based monolithic architecture, 5250-based ‘Green Screens’, tightly coupled Business Logic, and the high cost of Server/OS upgrades make the operation of legacy AS/400 application modernization challenges.
IBM i/AS 400 system modernization can be a complex task and requires diverse methodologies depending on the company’s requirements, risk profiles, and workload. The most common reasons we discussed in this article that can delay the AS400 application modernization projects are:
- Lack of a comprehensive business plan to handle future company requirements.
- Limited display view of the existing AS400 application landscape
- Unaware or ignoring the potential risk that may be involved
- Insufficient or lack of funding for long-term modernization business plans
- Lack of knowledge of real-time monitoring and analytics
LANSA’s IBM i modernization toolset provides a more efficient method to modernize your AS400/IBM i applications.
How do you apply AS400 application modernization?
Organizations can use the different modernization strategies to modernize the AS400 systems:
- Re-Hosting (lift-and-shift)
- Renew existing Application
- Re-Platform/Re-Engineering
- Re-Architecturing/Re-Factoring
To complete the AS400 application modernization task successfully, organizations must have a clearly defined set of rules with a dedicated plan, modernization strategy, and detailed knowledge about future architecture.
Different approaches to modernize the existing AS400/IBM i applications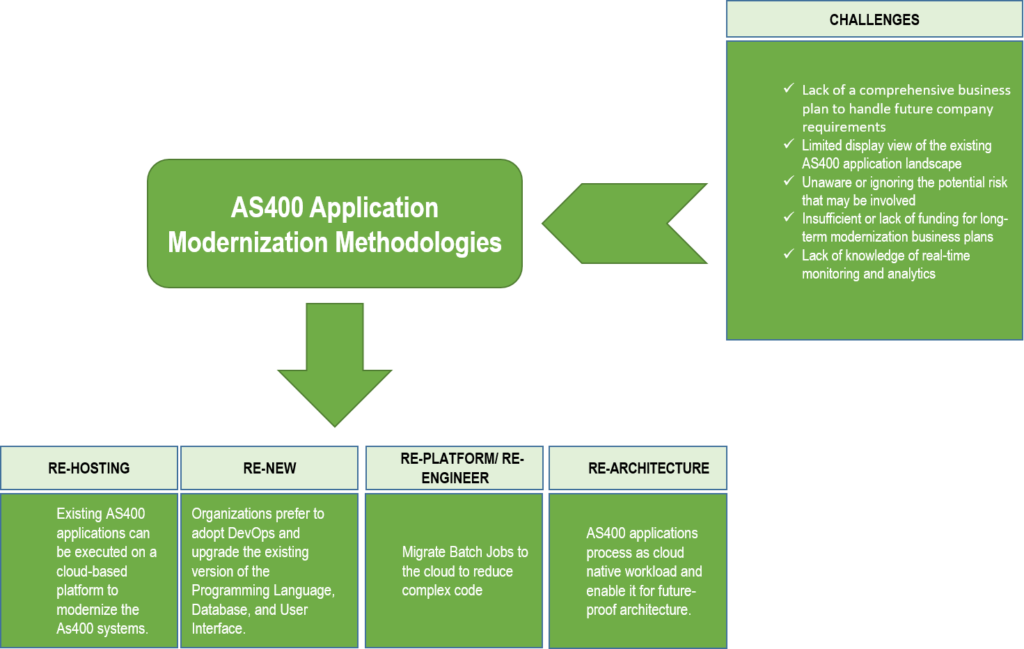
Re-Host (Lift and shift)
In the re-hosting methodology pattern, organizations migrate the AS400 legacy systems to the new cloud platform to reduce costs and scale up business use cases.
In this approach, existing AS400 applications can be executed on a cloud-based platform to modernize the AS400 systems.
Using an AS400 emulator that consists of a set of the compiler, OS (Operating System) services, and packages that allow application programs (RPG and COBOL for AS400 and database) to migrate with source code. These programs are recompiled and executed on the AWS platform, including the complete database (DB2/400) replication.
Third-party tools used by application components, such as message queues, backups, Reporting, schedulers, printing, and tape management, are also migrated to the cloud.
Re-new/Re-facing existing Application
In this methodology pattern, organizations prefer to adopt DevOps and upgrade the existing version of the Programming Language, Database, and User Interface. For UI modernizations, the 5250 screens are converted into a web interface without changes to existing application support. Organizations can upgrade the application’s RPG, and DB2 modules into modernized modular and decoupled components to modernize the existing AS400 applications.
Using a web portal and some User Interface adaptation, convert green screens DDS files to High Rich Display files. Using LANSA’s aXes, the AS400/IBM i 5250 screen panel can be converted into a modern web user interface. It transforms the existing 5250 screens into web pages out-of-the-box, without changing the source code.
Re-Platform/Re-Engineer-Migrate Batch Jobs
Batch jobs often form a large portion of the As400 application portfolio (such as ETL data processing, EDI file processing, and ad-hoc report generation), and while some are business-critical, usually a significant number of these jobs are of low business value due to their high cost and low agility.
Using any candidate solution, whether they are file-based or near real-time processes, to modernize the existing As400 application, physical files or real-time data streams are sent to the AWS cloud, respectively. It enables the customers to gain additional data insights in the form of reports.
Re-Architecture/Re-Factor
When an existing IBM i/AS400 application is no longer able to fulfill future business requirements or an agile target architecture, the reengineering or refactoring approach is used for AS400 application modernization. This methodology pattern will lead to a new application with similar performance and approximately equal or improved functionality.
Typically, the AS400 application is modernized using cloud-native techniques, such as microservices, docker containers, decoupling, data analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning services.
With Visual LANSA and RAMP’s ability to combine the old with the new addresses both your immediate tactical issues for green screen to GUI modernization as well as your long-term redevelopment and replacement strategies for 5250 modernization.
Want to learn more about application modernization techniques?
Download Application Modernization for Dummies, LANSA Edition eBook. Application modernization is not only about putting a pretty face to a 5250 screen. Application modernization also includes the transfer of legacy applications or platforms to modern applications or platforms, as well as the integration of new functionality to give the company the most up-to-date features.
Ready to get started modernizing your IBM i applications?
We explored different approaches such as Rehosting, Re-engineering, Re-architecture, and Re-new for AS400 application modernization. These methods enable different organizations to increase their business agility and performance and reduce cost and manual dependencies that enable their IT to drive business growth. If you want to modernize your IBMi/AS400 applications, you can contact us . Thanks!























